


Theme
Medical Physics
INSTITUTION
Department of Physics and Astronomy, King Saud University.
King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology, Saudi Arabia.
Department of Radiology, King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Centre, Saudi Arabia.

Shielding of medical imaging rooms is an important procedure in the clinical environment to product health practitioners and members of the general public from radiation exposure[1]. CT scanners are widely available, and the CT technology has evolved significantly over the last decades [2]. This includes performing scans with wide beams, i.e. cone beam CT (CBCT), which allows, for example, performing fast scans that minimize the motion artifact [3].
Several methods are used for shielding calculations for CT rooms, one of which is based on the dose length product (DLP) of scans along with scatter factors [1]. The aim of this study was to establish scatter factors for wide beam scans and compare them with those for scans acquired with narrow beams.
Three CT scanners at King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Center (KFSHRC) were utilized, two by GE (Lightspeed and Revolution) and one by Siemens (Somatom force dual energy). Scatter factors were determined by normalizing scatter air kerma resulting from scans with respect to their DLP values. An anthropomorphic whole body phantom was used to mimic the patient’s body.
Scatter air kerma was measured with an ion chamber survey meter placed 1 m away from the scan isocenter. Since scattered radiations resulting from CT scans spread around the scanner in a non-uniform pattern, measurements were made in three areas, at the front and the rare of the scanner gantry and beside the scanner gantry.
Therefore, the survey meter was rotated around the scanners to cover those areas. A number of head and body scan protocols that are used in the clinic were studied. This includes protocols performed with narrow and wide beams and dual energy.
The measurements of scatter air kerma per unit DLP are plotted against angle to the scan plane for 120 kV scans for:
- The Fan Beam for Body and Head.
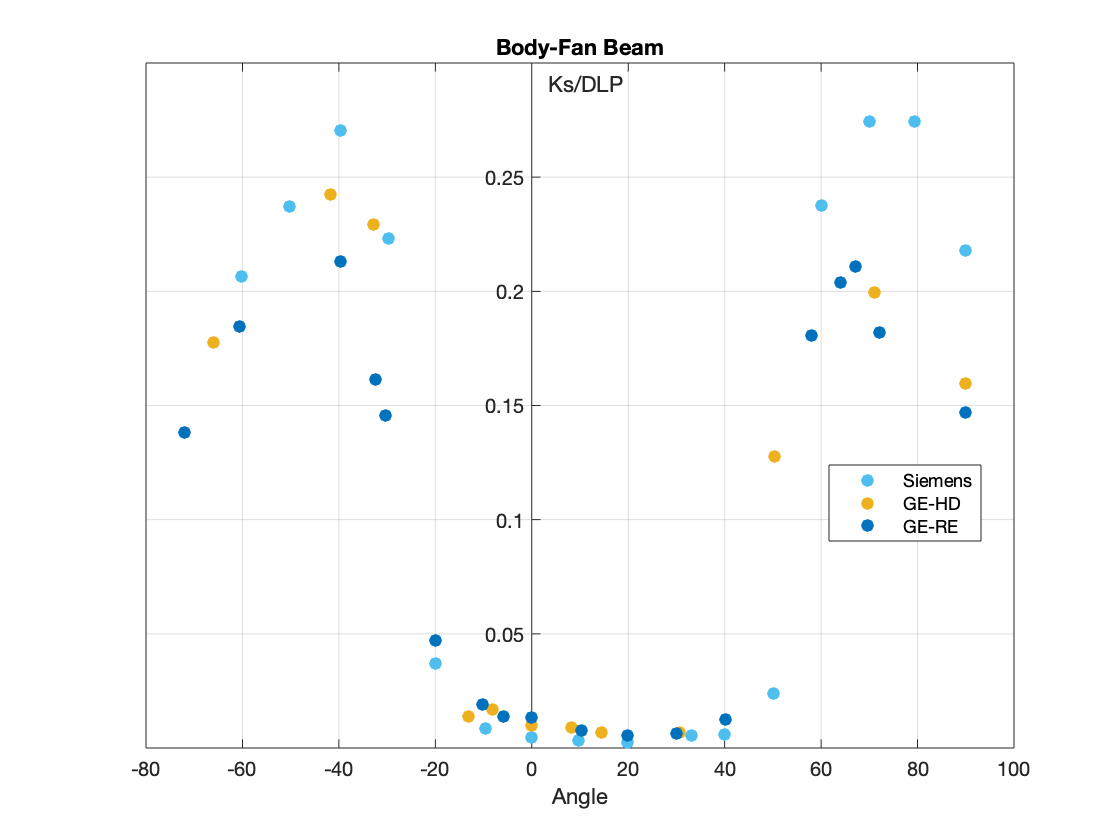
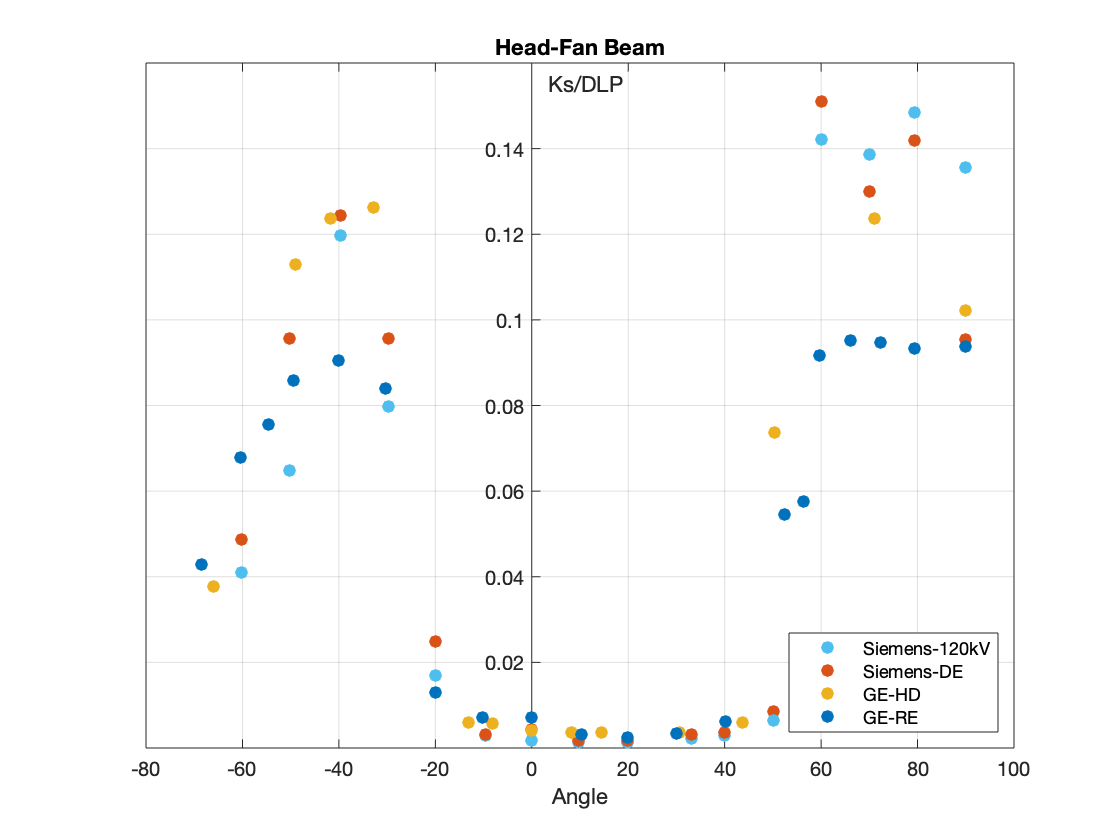
- The Wide Beam for Body and Head.
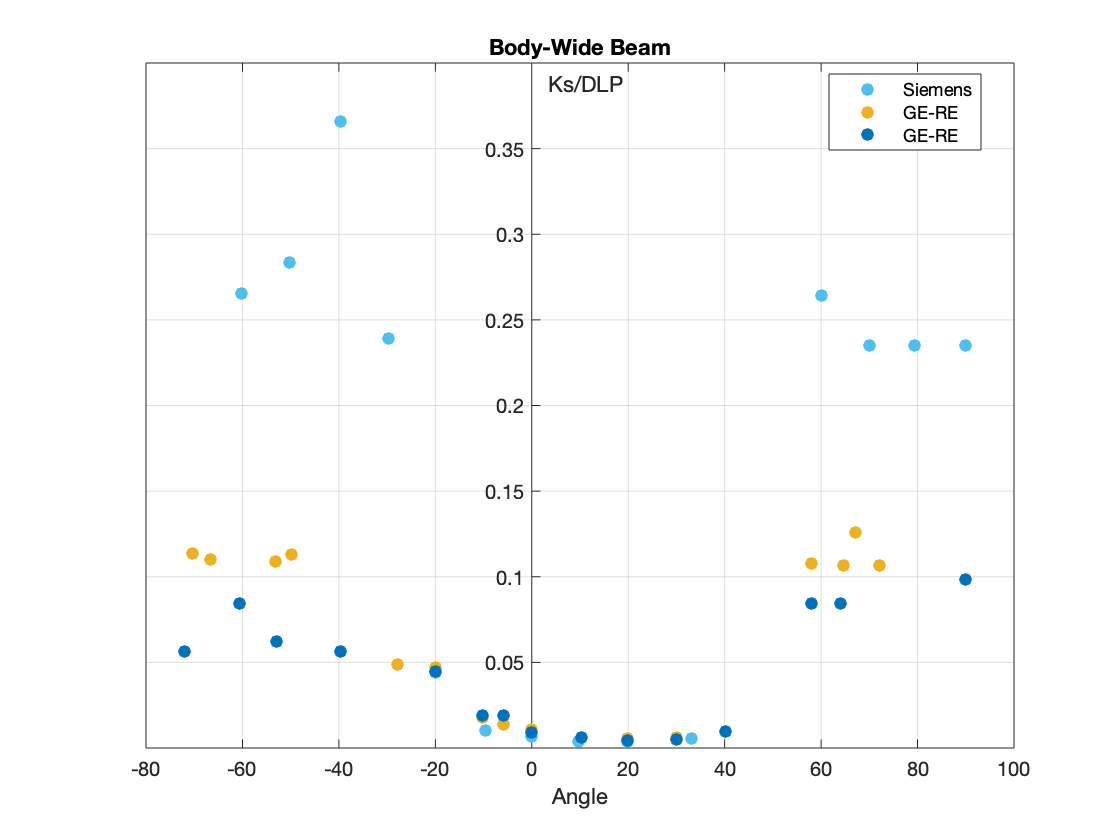
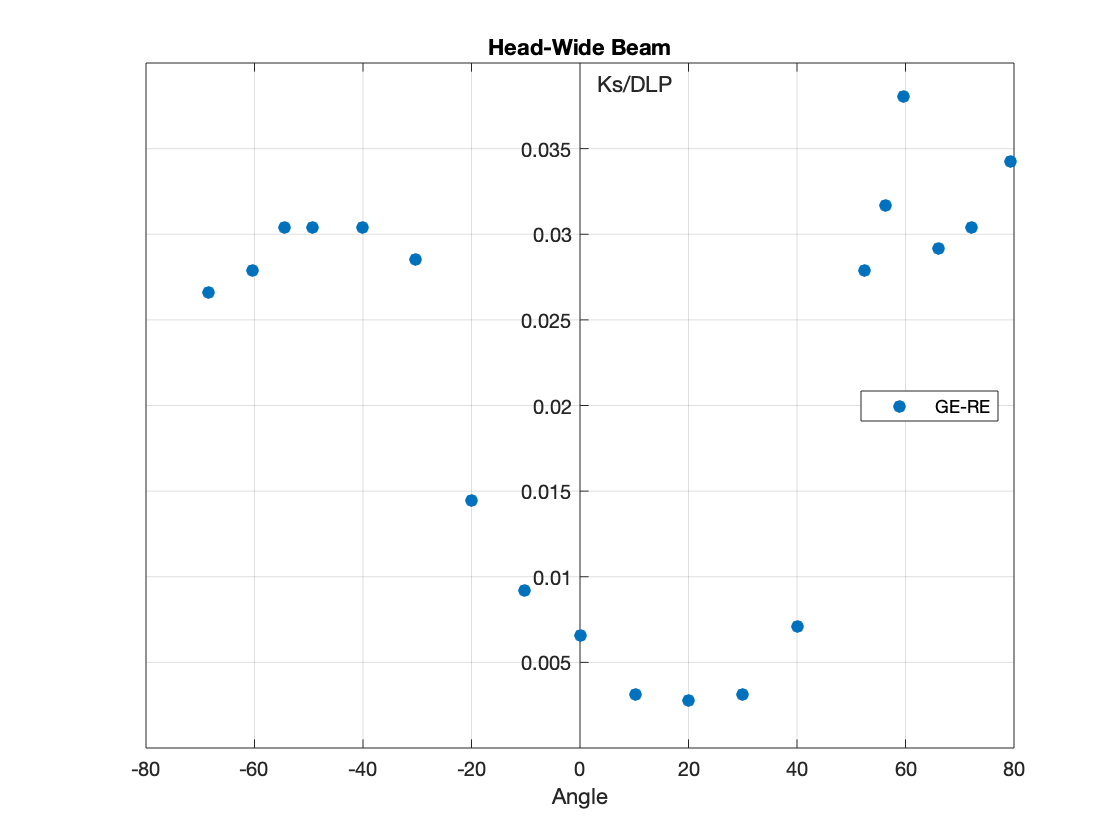
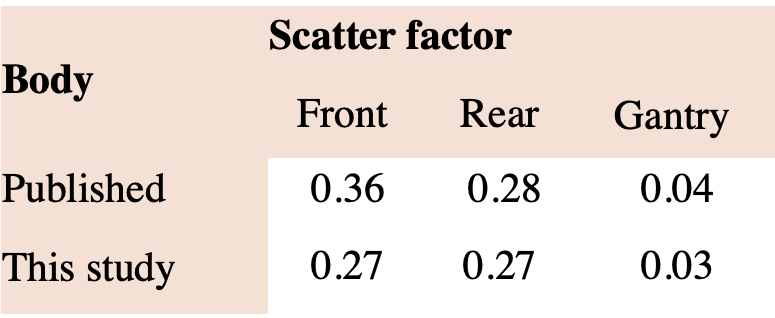
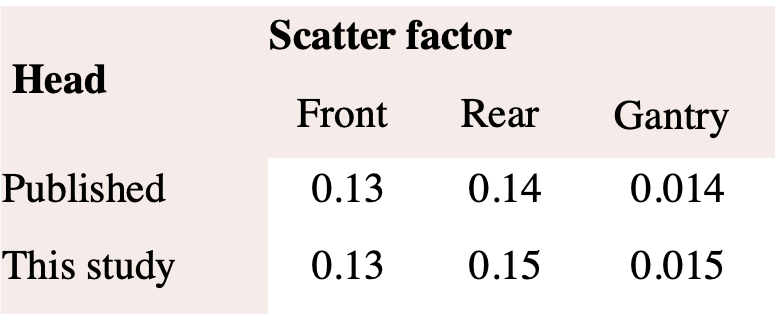
Scatter factors for scans acquired with narrow beams:
Scatter factors for cone-beam scans:
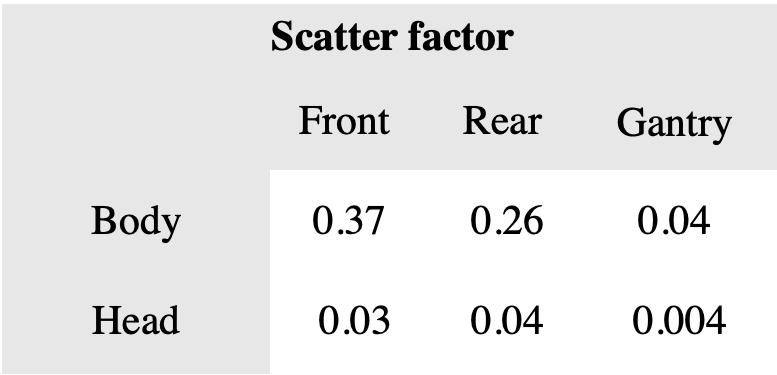
From the result of this study, it could be concluded that scatter factors of cone beam scans were comparable to those of the narrow beams for body scans, but lower for the head scans.
[1] N. C. on R. P. (US), Structural shielding design for medical x-ray imaging facilities, no. 147. NCRP, 2004.
[2] D. R. Dance, S. Christofides, A. D. A. Maidment, I. D. McLean, and K. H. Ng, “Diagnostic radiology physics,” Int. At. Energy Agency, 2014.
[3] W. C. Scarfe and A. G. Farman, “What is cone-beam CT and how does it work?,” Dent. Clin. North Am., vol. 52, no. 4, pp. 707–730, 2008.
[4] H. Wallace, C. J. Martin, D. G. Sutton, D. Peet, and J. R. Williams, “Establishment of scatter factors for use in shielding calculations and risk assessment for computed tomography facilities,”J. Radiol. Prot., vol. 32, no. 1, p. 39, 2012.
 Send Email
Send Email