
|
Authors | Institution |
|
Jood Alawami Leena Dakhaikh Raghad Barnawi Shahad Alkhaldi |
Imam Abdulrahman bin Faisal University |
 |
|
||||||
| Design and Development of a 3D-Printed Robotic Arm for Upper Limb Amputees |
 ONLY 1 out of 10 amputees has the ability to get an artificial limb, according to a statistical study conducted by the World Health Organization (WHO) [1]. This is due to several factors; the most prominent of them is the high cost of prostheses [2]. Our project aims to apply engineering principles in order to produce a cost-effective robotic hand with high performance, to provide access to prosthetic hands for a large segment of society.
ONLY 1 out of 10 amputees has the ability to get an artificial limb, according to a statistical study conducted by the World Health Organization (WHO) [1]. This is due to several factors; the most prominent of them is the high cost of prostheses [2]. Our project aims to apply engineering principles in order to produce a cost-effective robotic hand with high performance, to provide access to prosthetic hands for a large segment of society.
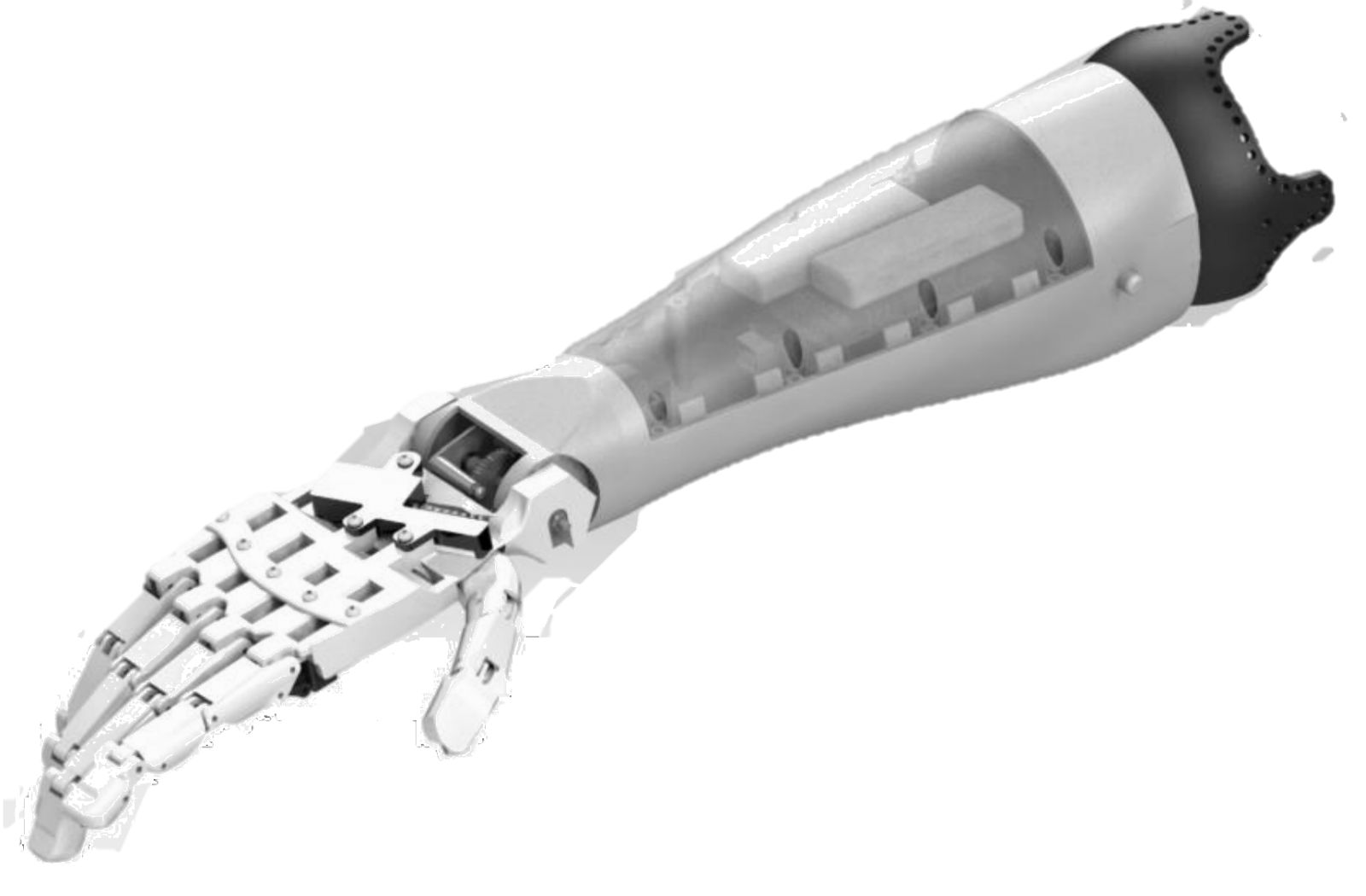 Introduced is a 3D-printed prosthetic upper limb controlled by myoelectrical commands using electromyography (EMG) signals. Because the prosthetic hand is 3D printed, it offers many prominent features, including faster production, lower cost, and being user-customized for cosmetic appearance. Executing the commands that are generated from two EMG signals using two different surface EMG sensors in the design allows a more controlled maneuver over the prosthetic for various hand movements, which reduces the mechanical effort normally required by the amputee. To achieve this control, a suitable algorithm that allows recognition of movement orders will be developed.
Introduced is a 3D-printed prosthetic upper limb controlled by myoelectrical commands using electromyography (EMG) signals. Because the prosthetic hand is 3D printed, it offers many prominent features, including faster production, lower cost, and being user-customized for cosmetic appearance. Executing the commands that are generated from two EMG signals using two different surface EMG sensors in the design allows a more controlled maneuver over the prosthetic for various hand movements, which reduces the mechanical effort normally required by the amputee. To achieve this control, a suitable algorithm that allows recognition of movement orders will be developed.

This electrically powered prosthetic arm uses sEMG signals for control to generate different prosthetic arm movement patterns. The conducted experiment helped in determining the suitable location for sensors and ensure their capability of providing needed different signals to different movement patterns. The acquired signal from the forearm was processed to compare between the signal amplitudes during different hand movement, which introduced the pattern recognition approach to increase the accuracy and decrease errors and random movements.


Control Method

1- Two EMG sensors acquire different signals from the two muscles.
2- EMG signals divided into three categories, low, medium and high
3- For each combination of categories a particular movement is resulted.
[1] "Standards for prosthetics and orthotics", World Health Organization, 2019. [Online]. Available: https://www.who.int/phi/implementation/assistive_technology/prosthetics-and-orthotics/en/. [Accessed: 24- Oct- 2019].
[2] C. Cipriani, F. Zaccone, S. Micera, and M. Carrozza, “On the Shared Control of an EMG-Controlled Prosthetic Hand: Analysis of User–Prosthesis Interaction,” IEEE Transactions on Robotics, vol. 24, no. 1, pp. 170–184, 2008.
 Send Email
Send Email
