
| Theme: Best Practice in Curriculum Planning, Development, Implementation, and Evaluation | |||
 |
||||||
| Students Perception Towards Problem-based Learning in Medical College at Al-Imam Muhammad Ibn Saud Islamic University |
 |
|||||
|
||||||
Problem-based learning (PBL) is a student-centered innovating instructional approach in which students define their own learning objectives by using triggers from the problem case or scenario. A PBL hybrid model is adopted in many undergraduate Medical Schools in Saudi Arabia. Our aim is to investigate the students’ perception toward the PBL sessions in the College of Medicine, IMSIU, Riyadh, KSA.
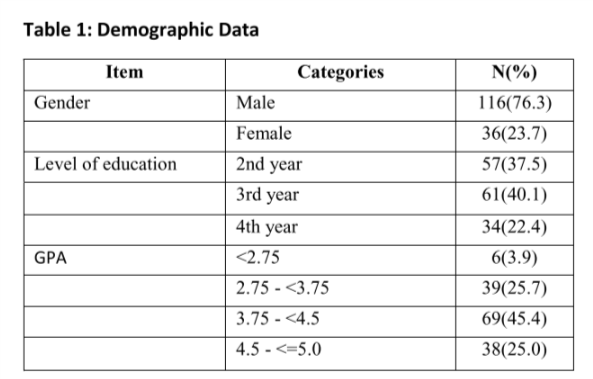
We conducted a cross-sectional study based on a self-administered questionnaire in the first semester of 2017-2018 academic year in the College of Medicine at IMSIU, Riyadh, KSA. The data collection tool was administered to second, third male and female students, as well as the fourth year medical male students.. The questionnaire was divided into 5 parts:- demographic data, student’s perception to PBL session benefits, student’s perception to the appropriately running of PBL sessions, tutors facilitation of the PBL sessions and their fairness on students’ evaluation, and utilization of self-directed learning resources, duration, and preferred places. The data was analyzed by SPSS software.
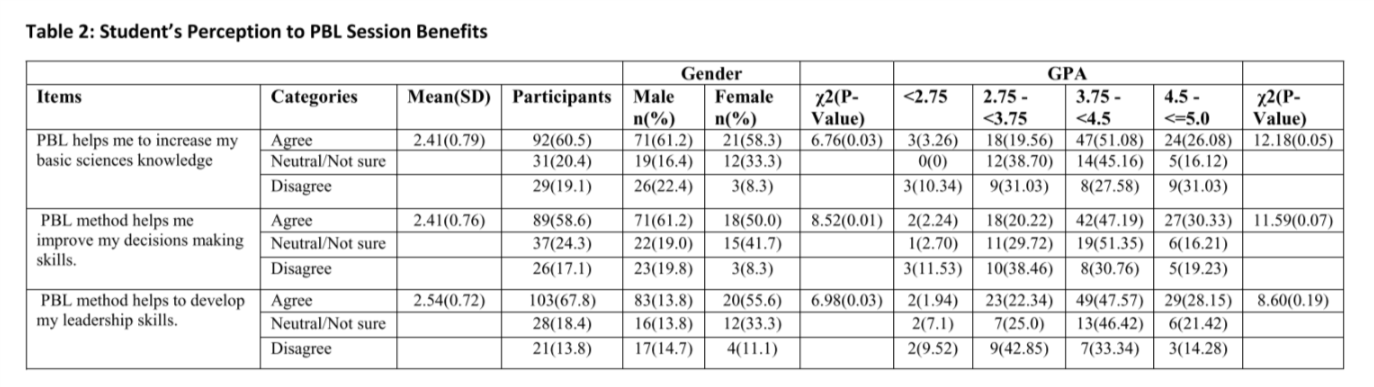
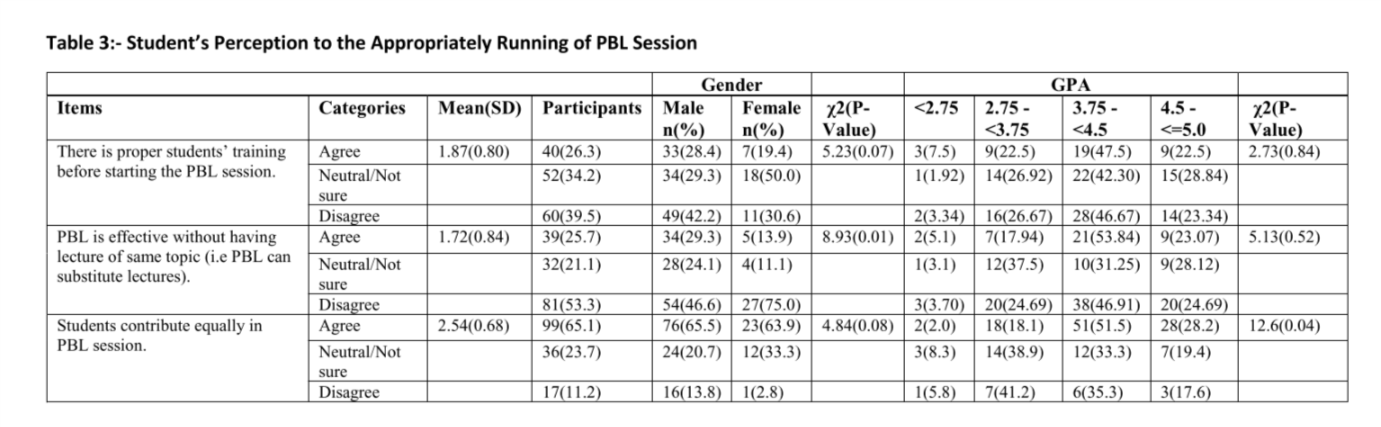
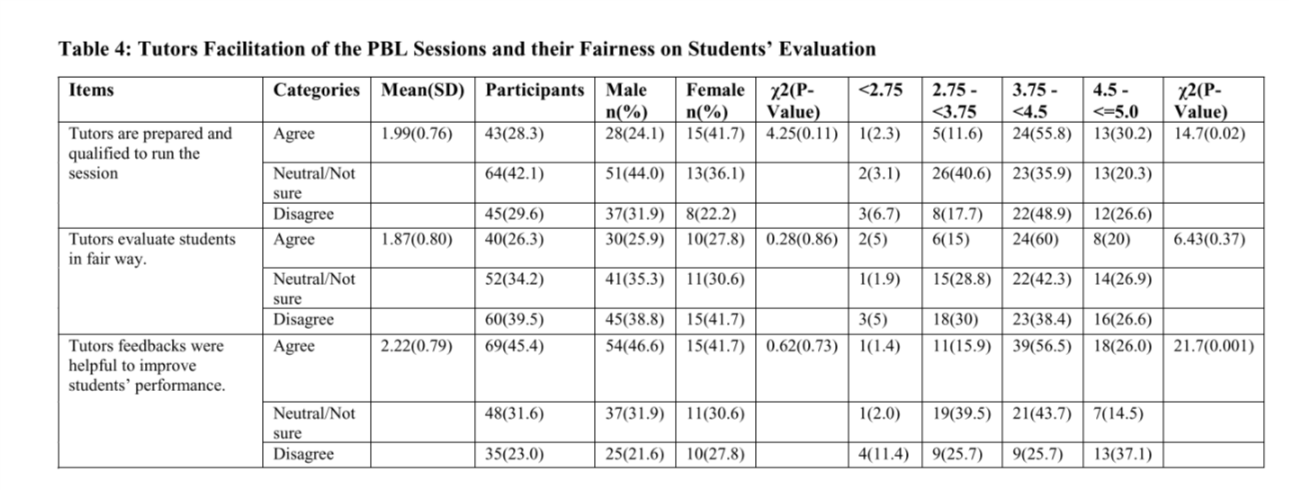
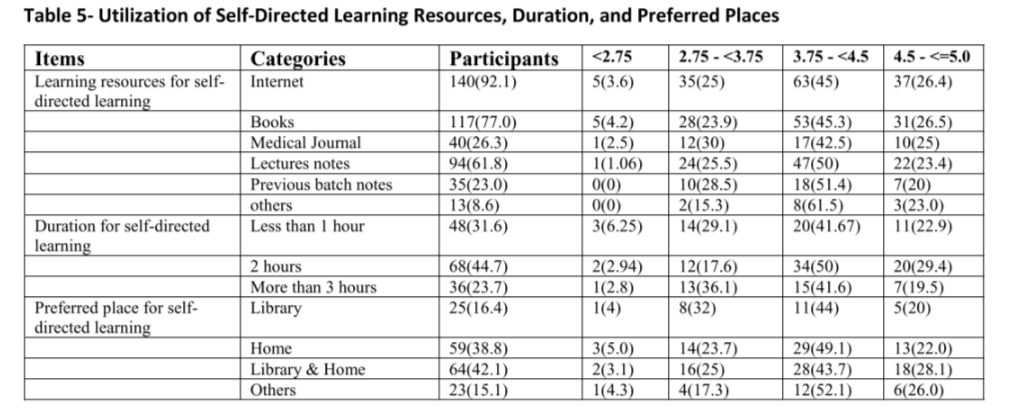
Out of 259 Students, 152 (59%) completed the questionnaire. (58.6%) Agreed that PBL was helpful in improving decisions making skills (p= 0.01). Only (26.3%) of the students reported that there is a proper students’ training before starting the PBL session. (53.3%) Disagreed that PBL is effective without having a lecture on the same topic (p=0.01). Only (28.3%) of the students agreed that the teaching staff is well prepared to run the sessions. The most commonly used resource for self-directed learning was internet (92.1%), followed by books (77%) and lecture notes (61.8%).
This study showed that tutors should be trained to guide the process of PBL in order to achieve its goals. The students should be securely introduced to PBL and experience the development of their clinical reasoning through PBL. Further longitudinal studies should be carried out in medical colleges all over KSA to obtain more valid outcomes.

 Send Email
Send Email