
| Theme: Biomedical Engineering | |||
 |
||||||
| Diffuse Optical Imaging for Medical Applications |
 |
|||||
|
||||||
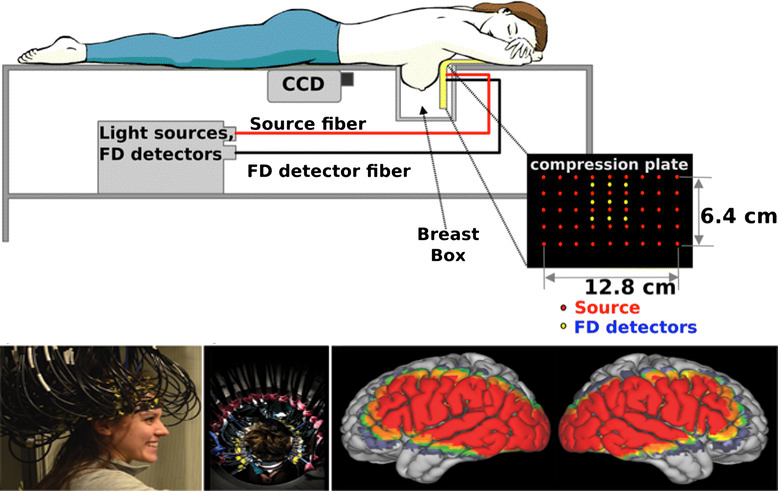
DOT is a non-invasive techniques that utilizes light in the near infrared spectral region (700 nm to 1100 nm) to measure the optical properties of physiological tissue. It has the advantages of being non-ionizing, portable, low-cost, and this is becoming a very useful supplement that is currently emerging as a promising new addition to medical imaging.
DOT is based on the principle of diffusing infrared light. The source infrared pass the skin to interact with the tissues at multiple projections in order to produce a tomographic image. Interaction happens when light gets absorbed by chromophores such as hemoglobin and water molecules, or scattered due to various cellular structures in tissues. The light is guided by fiber optics to the surface of the subject such as the brain or breast. DOT uses arrays of sources (light) and detectors placed around the object. The received data or signals are sent to the data acquisition to produce an image. It has been applied in various deep-tissue applications including breast cancer imaging, brain functional imaging, stroke detection and others.
1. Imaging of in vitro and in vivo bones and joints with continuous-wave diffuse optical tomography
This paper aims to show that diffuse optical tomography (DOT) has the potential to be used for detecting and monitoring bone and joint diseases such as osteoporosis and arthritis.
● System used: DOT imager system
● Sample used: In vitro - two chicken bones
In vivo - index finger of a volunteer ( male )
● Tomographic measurements were taken at different planes.
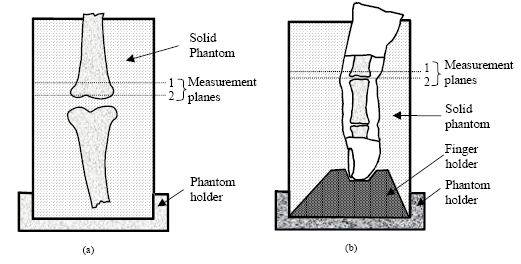
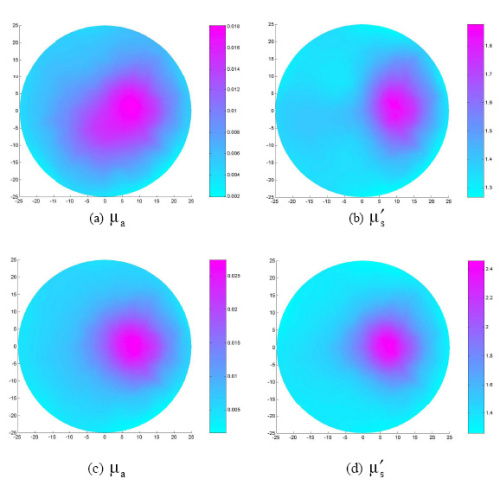
1. Imaging of in vitro and in vivo bones and joints with continuous-wave diffuse optical tomography
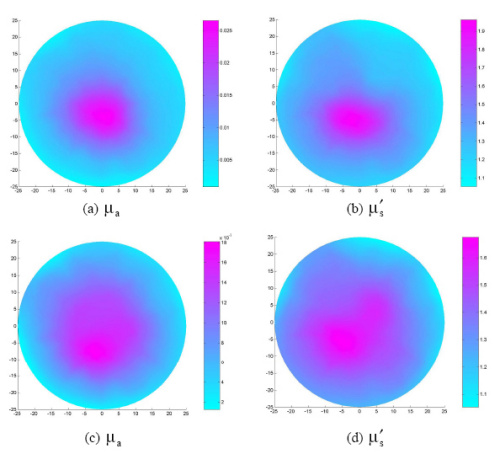
In vitro study
-
The absorption or the scattering increase at the bone region compared to the phantom background.
-
The bone size resolved (1.5cm) by DOT is comparable to the actual bone size (1.6cm)
In vivo study -
A significant absorption or scattering increase in the joint and off-joint bone compared to the surrounding soft tissue and phantom background.
-
The imaged bone size (1.65cm) is comparable to the actual size of bone in the finger (1.7cm).
In this review poster, a clear background of diffuse optical imaging system is provided. Data was collected and represented through different scientific journals to represent the system basic principles, techniques and applications. Various applications have been reviewed through the journals including studies of joints, breast, and brain. Diffuse optical imaging was used accompanied by techniques like fluorescence and continuous waves and compared with current techniques like MRI and X-Ray. Results from the reviewed journals prove that diffuse optical imaging is an effective tool and the future of medical imaging.
[1]"Diffuse Optical Tomography: Image Reconstruction and Verification", Ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, 2007. [Online]. Available: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4290522/#s1title.
[2]."Imaging of in vitro and in vivo bones and joints with continuous-wave diffuse optical tomography", Osapublishing.org, 2001. [Online]. Available: https://www.osapublishing.org/oe/fulltext.cfm?uri=oe-8-7-447&id=63910.

 Send Email
Send Email