| ePOSTER | ||
| Theme: 7AA eLearning: Games, resources and platforms |

|
| Abstract Title |
 |
|
| Subjective assessment of students' ability to use ICT during the 1st year of the medicine study | ||

|
Authors: |
Zuzana Balazsiova Eva Kralova |
Institutions: | Comenius University, Faculty of Medicine - Institute of Medical Physics, Biophysics, Informatics and Telemedicine - Bratislava - Slovakia |
Teaching of Informatics in High school in Slovakia is focused on using common application programs in limited range. The aim of study is to assess the readiness of the 1st year students to use ICT in the study of medicine and their ability to obtain correct information from appropriate sources.
Questionnaires investigated level of used internet web pages by students for their study. 185 questionnaires were evaluated. Students assigned score to each question (0 in the scale - doesn´t used, doesn´t known; 10 in the scale - the mostly used, level of expert)
Questions that were evaluated in this study:
- Rate your own experience with the using search engines on the internet: a) search engine tools, b) web portals, c) online library, d) biomedicine databases.
- Name the professional biomedical databases, which you know.
- Rate your experience with the using of biomedical databases.
- Students used for their school works mainly Internet search tools (average score 9.27) and web portals (average score 7.09). Other searching tools are neglected by students (online libraries – average score 2.52; biomedical databases – average score 1.31). The level of use of biomedical database is very different. Only one student (0.54%) rated the degree of use online library catalogs and biomedical databases for 10 points. This means that e-libraries and databases are commonly used by him. 72 students (38.92%) do not use the electronic catalogs of libraries and 126 students (68.12%) do not use biomedicine databases absolutely (score = 0 point). The Figure 1. shows the scores (average and standard deviation) which students assigned to themselves.
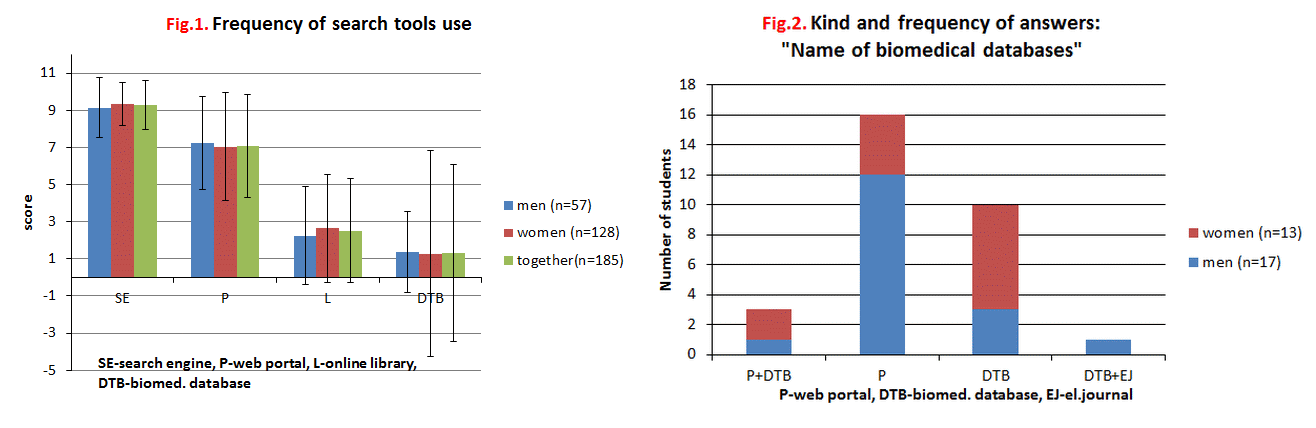
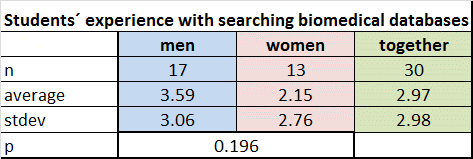
- 16.22% students (30/185) answered the question: “Name the professional biomedical databases, which you know” 10 of them answered names databases correctly. Other students gave names web portals, dictionaries, encyclopaedias…(Figure 2.)
The names of the databases (DTB) that are known to 14 students: PubMed, Web of Science, medical dictionaries, Medline, Reaxys
The names of the web portals (P) that are known to 19 students: Biopedia, Bioweb, e-Health, Mefanet, Sceletopedia, Medscape, Wikipedia, Wikiskripta, web pages of libraries
- Students who answered to question 2, rated their searching experience in biomedical databases. In generally, these students used databases for their study very little (average score of 2.97 points from 10 point scale) Men rated their experience by higher scores than women. This difference was not statistically significant. (Table)
The students have usually problem to acquire information, which is needed for their study. They created projects and papers at high school, but there were used only general web portals (e.g. Wikipedia) and other encyclopaedias. Their experience in the use of scientific databases and libraries are minimal and inadequate.
The 1st year medical students could learn searching relevant and current medical scientific sources in professional medical databases and libraries for the purposes of their study in the introductory course.
This study was supported by KEGA MŠVVaŠ SR 052UK-4/2013.
 Send Email
Send Email