
| Theme: 5JJ Interprofessional education 2 | |||
 |
||||||
| The effect of interprofessional Education (IPE) activity on the opinions held by Health Care students on IPE |
 |
|||||
|
||||||
In the last decade many universities have begun to integrate IPE into their curricula. The World Health Organization (WHO) has bolstered it and has published a ‘Framework for Action’ position paper which emphasizes how important IPE is for patient safety, health system efficiency and for the promotion of medical education in universities throughout the world.
The Faculty of Health Sciences’ administration, in partnership with, and with encouragement from, the Goldman Foundation, has decided to promote this subject and, in fact, it is the first faculty in Israel to incorporate a multi-year IPE course in its curriculum.
The students completed an opinion questionnaire before and after the activity. The questionnaire was translated, and adapted, from the Readiness for Interprofessional Learning Scale (RIPLS) Questionnaire. For the purpose of statistical analysis we created 3 categories: "agree" (which included "strongly agree" and "agree"), "disagree" (which included "disagree and strongly disagree") and "uncertain".
131 students from the Health Sciences faculty at Ben Gurion University participated in the study. There were 39 (30%) males and 91 (70%) females. The average age was 26.06 ± 2.65. There were 55 (42%) students from the medical, 46 (35.1%) students from the nursing and 30 (22.9%) students from the physiotherapy schools.
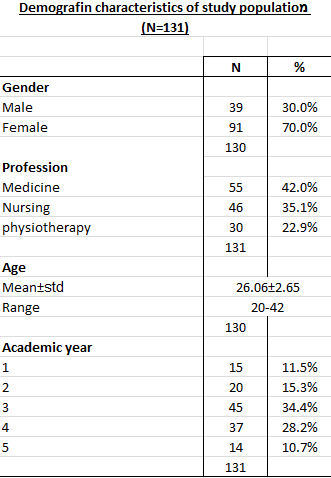
Prior to the activity 13 students (10%) agreed with the statement “Communication skills should be learned with other health care students” vs. 25 (19.1%) after the activity (p<0.05).
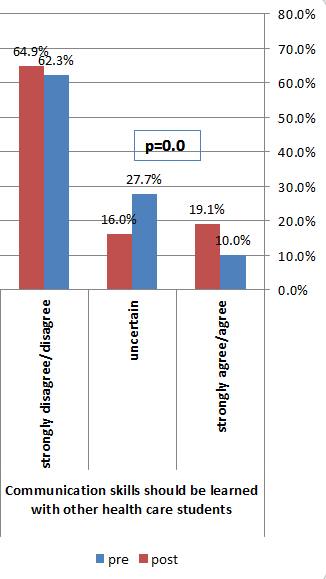
Three students, prior to the activity, (6.2%) agreed with the statement “Shared learning will help me understand my own limitations” vs. 15 students (11.5%) after the activity. (p<0.05).
Nine students, prior to the activity, (6.9%) agreed with the statement “Shared learning will help me to think positively about other professions” vs. 21 students (16.2%) after the activity (p<0.05).
The remaining questions did not have a statistically significant difference.
IPE activity among health care students affects their opinion of IPE in a positive way.

Siaal Research Center for Family Medicine and Primary Care

 Send Email
Send Email