
| Theme: 2II Evaluation of teaching/Educational research | |||
 |
||||||
| Challenges in an educational RCT |
 |
|||||
|
||||||
Societal changes demand efficient surgical training. Module based skills training combined with clinical operative training may be a future model. This study set out to measure the effect of such a module based training program applied in laparoscopic cholecystectomy in surgical registrars.
Due to heavy drop-outs only ten participants completed the study and furthermore the inter-rater reliability showed Cronbach’s alpha=0.37 in spite of three independent raters. However, data do show effect of the fast-track program on technical skills compared to standard training at one year follow-up despite equal number of performed procedures in the two groups (p=0.010).
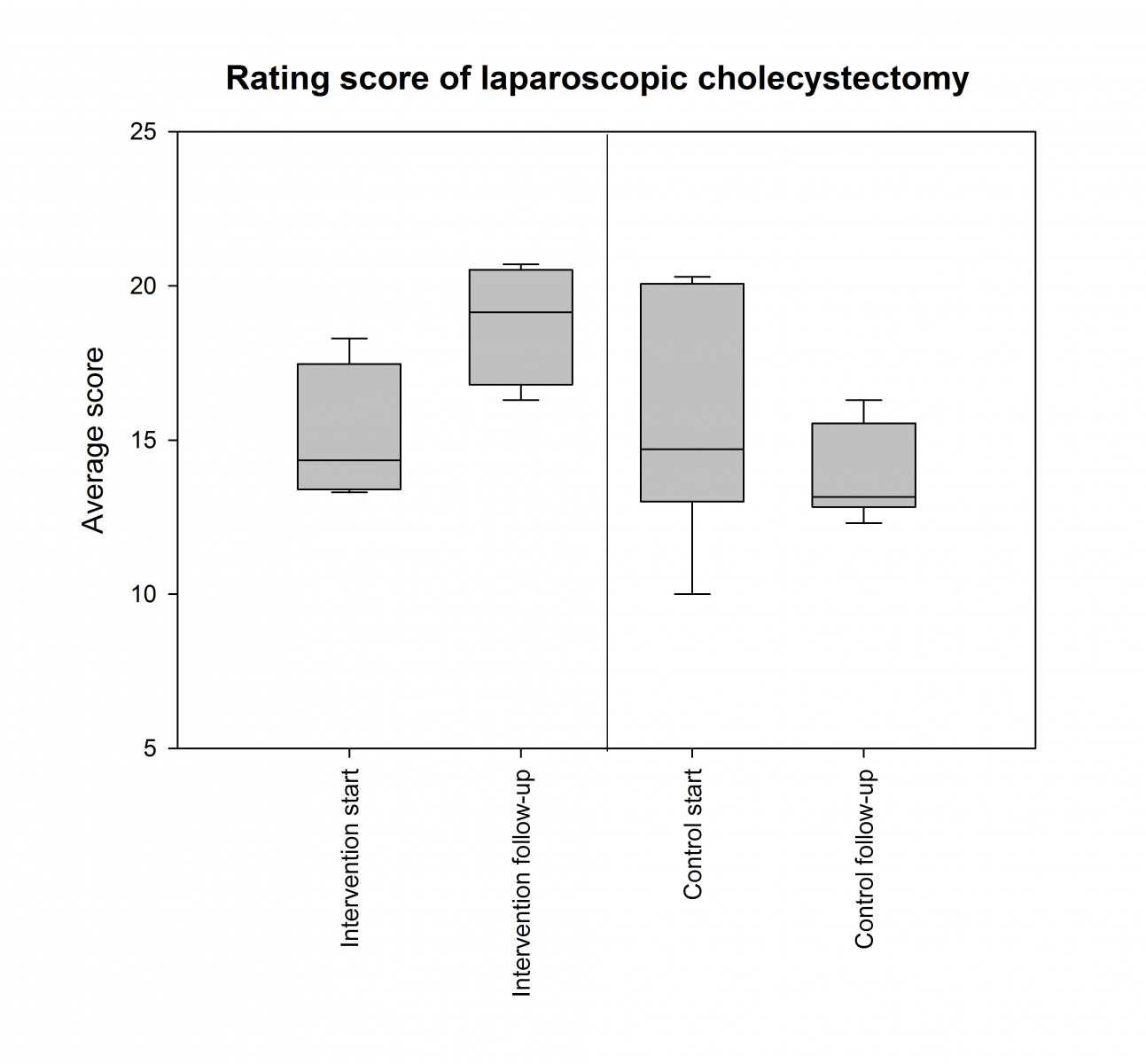
35 Danish surgical specialty trainees (registrars) were randomized to either a fast-track module with performance of 20 procedures or standard clinical training. The performed laparoscopic cholecystectomies were blindly rated by three trained raters using a former validated assessment tool, GOALS.
This study highlights some major challenges in educational randomized studies as only few trainees completed the study and inter-rater reliability was low. Especially use of an “of the shelf”-assessment tool was challenging and rater training seems to be an important issue. Rater training must be thoroughly designed. In conclusion: Module based training seems to be a promising surgical training design, though rater training needs more attention across different cultures.
Randomized educational studies face many challenges.


 Send Email
Send Email